Devices for high-frequency heat therapy
High-frequency heat therapy enables the precise heating of tissue areas close to the surface as well as in depth. This physical-therapeutic method is particularly suitable for subacute and chronic rheumatic diseases of the joints and muscles, circulatory disorders and numerous unspecific, subacute and chronic disease processes of internal organs, i.e. for all diseases for which heat therapy is indicated.
Acute inflammatory processes should either not be treated at all (e.g. acute rheumatoid arthritis) or only with very low doses. Here, the impulse mode has advantages, because with it the heat stimulus occurring in the tissue can be significantly reduced. It is therefore spoken of an indication expansion to acute disease processes.
Information:
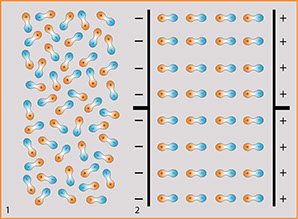
- The dipole molecules are initially arranged randomly in the body.
- Under the effect of an electric field, they rotate in the direction of the field lines depending on their polar charge. In the process, positively charged parts of the dipole turn towards the (respective) negative pole and negatively charged ones arrange themselves towards the (respective) positive pole. As the electric field changes its polarity, microheating occurs due to the constant new orientation of the molecules.
The heat distribution during therapy with short waves and microwaves:
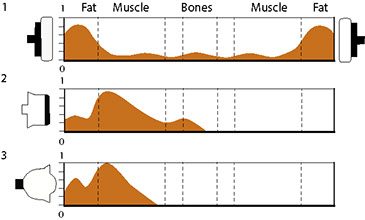
1. Ultratherm® Short-wave capacitor field
The body part located between two plate electrodes is completely flooded. Deep effect on fat load
2. Ultratherm®Shortwave Coil Field (DIODE®, MONODE®, and DIPLODE®)
Penetration depth and heat distribution are limited to near-surface, fluid-rich tissue areas. Near-surface heating during fat relief.
3. Radiotherm® Microwaves
Heat turnover is limited to near-surface, fluid-rich tissues. Near-surface heating during fat unloading.
The effects of high-frequency heat therapy:
- Increased cell metabolism
- Acceleration of chemical reactions
- Analgesia
- Change in cell membrane potentials
- Spasmolysis
- Enhanced leukocyte delivery
- Increased phagocytosis
- Attenuation of virulence of bacteria
- More rapid conversion of medicines
- Activation of endocrine gland activity
- Normalisation of vegetative dysregulations




